Dwight David “Ike” Eisenhower (1890 – 1969) was an American military general and politician who led the Allied Forces to victory in World War II and served as the 34th President of the United States from 1953 to 1961. Eisenhower served as the Supreme Allied Commander of the Allied Expeditionary Force from December 1943 till the end of World War II in May 1945. He planned and supervised the successful liberation of German occupied Western Europe. As president, Eisenhower deterred conflicts with the Communist Bloc through his New Look policy and kept America largely at peace. The most prominent achievement of his foreign policy was ending the Korean War by threats of using nuclear weapons. On the domestic front Eisenhower oversaw a period of economic growth; introduced important legislation regarding civil rights; founded the NASA; and championed the formation of the Interstate Highway System. Here are the 10 major accomplishments of Dwight D. Eisenhower including his military career; and the foreign and domestic policy during his presidency.
#1 He LED THE ALLIED FORCES TO VICTORY IN WW2
Dwight D. Eisenhower graduated from the United States Military Academy in 1915. In 1935, he was appointed assistant military adviser to the Philippine government under Douglas MacArthur. He returned to the U.S. in 1939 shortly after the advent of the Second World War. After the U.S. entered the war in December 1941, Chief of Staff General George C. Marshall appointed Eisenhower to the War Plans Division in Washington where he was charged with the responsibility for creating the major war plans to defeat Germany and Japan. In November 1942, he was appointed Supreme Commander of the Allied Force of the North African Theater of Operations. Eisenhower successfully led Operation Torch, the Allied invasion of French North Africa. He then oversaw the successful invasion of Tunisia, Sicily and the Italian mainland. In December 1943, Dwight D. Eisenhower was made the Supreme Allied Commander of the Allied Expeditionary Force. In this capacity he commanded Operation Overlord, the successful liberation of German occupied Western Europe; and the invasion of Germany. Eisenhower served as the Supreme Commander until the end of World War II in May 1945.
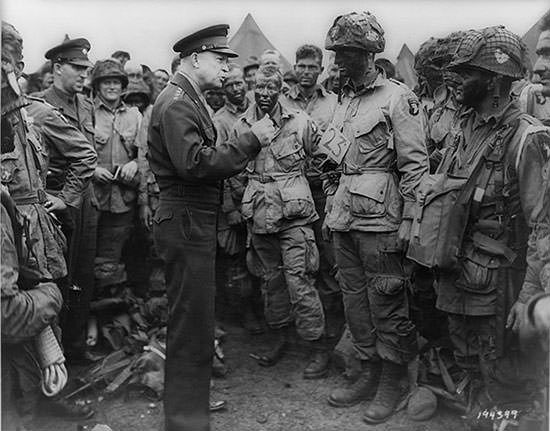

#2 HE SERVED AS THE FIRST SUPREME COMMANDER OF NATO
Though Eisenhower never saw combat during his military career, he was exceptional at military strategy and organization. The five-star officer rank was created in U.S. armed forces during the Second World War and Eisenhower is one of only nine people to have held this rank. After the war, Eisenhower served as the 16th Chief of Staff of the Army from November 1945 to February 1948. In 1948, he became President of Columbia University. The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) was founded in April 1949 and the following year President Harry S. Truman appointed Dwight D. Eisenhower as the first Supreme Commander of NATO giving him operational command of NATO forces in Europe. Eisenhower retired from active service as an army general on May 31, 1952, and he resumed his presidency of Columbia University. He held this position until he became President on January 20, 1953.

#3 HE SERVED AS THE 34TH PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES
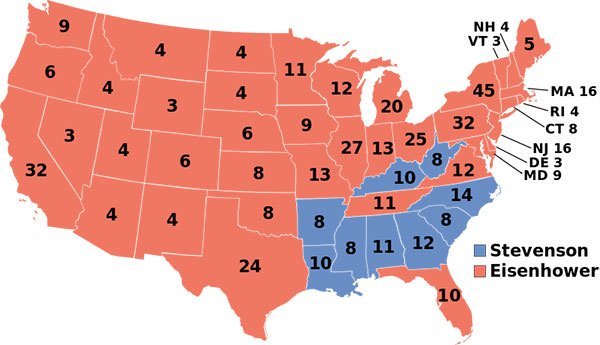
In the U.S. presidential election of 1952, Eisenhower won a landslide victory against Democratic candidate Adlai Stevenson II with an electoral margin of 442 to 89 and over 55% of the popular vote. In 1956, Eisenhower faced Adlai Stevenson again and won by an even larger landslide, with 457 of 531 electoral votes and 57.6% of the popular vote. Dwight D. Eisenhower served as the 34th President of the United States from January 20, 1953 to January 20, 1961. Eisenhower ended a string of Democratic Party wins that stretched back to 1932 becoming the first Republican to return to the White House in 20 years. He is also the only military general to serve as President of the U.S. in the 20th century.
#4 HE DETERRED CONFLICTS WITH COMMUNIST BLOC THROUGH HIS NEW LOOK POLICY
The national security policy of the United States during the presidency of Eisenhower is known as the New Look. Its most prominent aspect was stated in the U.S. National Security Council document NSC 162/2 of October 30, 1953 which says that the U.S. “will consider nuclear weapons as available for use as other munitions.” The U.S. Cold War policy of New Look thus threatened massive retaliation and use of nuclear weapons to deter the Communist Bloc led by the Soviet Union. Other major aspect of the New Look was balancing the Cold War military commitments of U.S. with the nation’s financial resources. Though the New Look has been criticized for limiting the options of America such as in the Hungarian Revolution of 1956, it kept U.S. out of Korea type wars as it was prepared to escalate its way out of the situation and took off pressure of the U.S. economy which had been bogged down due to military spending.
#5 He USED NUCLEAR THREAT TO END THE KOREAN WAR
During his presidential campaign Eisenhower had promised to end the stalemated Korean War. On November 29, 1952, president-elect Eisenhower visited Korea to assess the situation. He then used threats of a nuclear attack to make China come to terms. The United Nations Command, supported by the United States, the North Korean People’s Army, and the Chinese People’s Volunteers, signed the Korean Armistice Agreement on 27th July 1953 to end the fighting. The armistice established the Korean Demilitarized Zone to separate North and South Korea, put into force a cease-fire and finalized repatriation of prisoners of war. Eisenhower listed peace in Korea as his greatest presidential achievement.

#6 HE FOUNDED THE NASA IN 1958
The Space Race refers to the 20th-century competition between the Soviet Union and the United States for supremacy in spaceflight capability. The Soviets beat the U.S. in launching the first artificial Earth satellite, Sputnik 1, on 4th October 1957. This led to anxiety in America over technological gap between the two nations. President Eisenhower responded by creating, on February 7, 1958, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), which is responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military. He then signed into law the National Aeronautics and Space Act of 1958 which established the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), a civilian space agency responsible for the space program, as well as aeronautics and aerospace research. NASA has since grown into one of the most famous organizations in the world and is behind most U.S. space exploration efforts including the Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station and the Space Shuttle.

#7 He CHAMPIONED FORMATION OF THE INTERSTATE HIGHWAY SYSTEM
On June 29, 1956, President Dwight D. Eisenhower enacted the Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1956 authorizing the construction of the Interstate Highway System, a network of controlled-access highways that forms a part of the National Highway System of the United States. Initially US$25 billion were allotted for the construction of 41,000 miles (66,000 km) over a ten year period. It was the single largest public works program in U.S. history. The original portion of the project was completed in 35 years. The network has since been extended and as of 2013, it had a total length of 47,856 miles (77,017 km). Also, as of 2013, about one-quarter of all vehicle miles driven in the country use the Interstate system. The Interstate Highway System was a remarkable success. Among other things, the cost of traveling and shipping fell sharply; sub-urbanization became possible with cheaper housing as compared to the overcrowded cities; and tourism expanded dramatically. The system has also been used to facilitate evacuations in the face of hurricanes and other natural disasters. The Interstate Highway System is considered one of the greatest contributions of Eisenhower.

#8 HE ENACTED THE FIRST SIGNIFICANT CIVIL RIGHTS LEGISLATION SINCE 1875
In May 1954, the U.S. Supreme Court declared separate public schools for black and white students to be unconstitutional. In September 1957, Eisenhower sent federal troops to Arkansas to enforce this court ruling which mandated school desegregation. On September 9, 1957, Eisenhower passed into law the Civil Rights Act of 1957 primarily to ensure that all Americans could exercise their right to vote. This act was the first federal civil rights legislation passed by the U.S. Congress since the Civil Rights Act of 1875. By 1957 only about 20% of African Americans were registered to vote as most blacks had been effectively disfranchised by discriminatory voter registration rules and laws in many states. The 1957 Civil Rights Act set up a six-member Civil Rights Commission to gather information on deprivation of citizens’ voting rights based on color, race, religion or national origin. Subsequently the U.S. Department of Justice Civil Rights Division was established to enforce federal statutes prohibiting discrimination. On May 6, 1960, Eisenhower enacted the Civil Rights Act of 1960 that established federal inspection of local voter registration polls and introduced penalties for anyone who obstructed someone’s attempt to register to vote.

#9 ALASKA AND HAWAII WERE ADMITTED AS STATES OF U.S.
Other major legislation in domestic policy during the Eisenhower presidency include the Refugee Relief Act of 1953, which resulted in the admission of 214,000 immigrants to the United States mostly from European countries; the National Defense Education Act of September 1958 which provided funding to U.S. education institutions at all levels and aimed to improve the American education system particularly in the areas of science and technology; the Alaska Statehood Act of 1958 that allowed Alaska to become the 49th U.S. state on January 3, 1959; and the Hawaii Admission Act of 1959 which dissolved the Territory of Hawaii and established the State of Hawaii as the 50th state to be admitted into the Union. Also, Eisenhower founded the People to People International (PTPI) on September 11, 1956 as part of the United States Information Agency. PTPI aims to enhance international understanding and friendship through educational, cultural and humanitarian activities involving the exchange of ideas and experiences directly among peoples of different countries and diverse cultures.

#10 He IS REGARDED AS ONE OF THE GREATEST PRESIDENTS
Eisenhower was a self-described “progressive conservative” and he stuck to the policy of dynamic conservatism through his presidency. He signed legislation that expanded Social Security, increased the minimum wage, and created the Department of Health, Education and Welfare. He also supported government construction of low-income housing but favored more limited spending than his predecessor Harry S. Truman. Apart from mild recessions in 1953-1954, 1957-1958 and 1960, the economy expanded robustly during his term as president. Unemployment was generally low, inflation usually was 2 percent or less and poverty rate declined. Wage earners enjoyed a prosperous decade and personal income increased by 45 percent. Eisenhower is considered one of the greatest presidents of the United States and he is usually rated in the top 10 in surveys of academic historians and political scientists or popular opinion.

EISENHOWER’S CRUSADE IN EUROPE
After the end of World War II, General Dwight D. Eisenhower published a book of wartime memoirs titled Crusade in Europe. It recounted his appointment by General George Marshall to plan the defense of the Philippines and described his execution of the role of Supreme Allied Commander in Northern Europe. Crusade in Europe became an international bestseller and was adapted into a 26-episode TV series with the same title that won a Peabody Award and an Emmy Award.


The article left out President Eisenhower’s role in creating the Saint Lawrence Seaway.