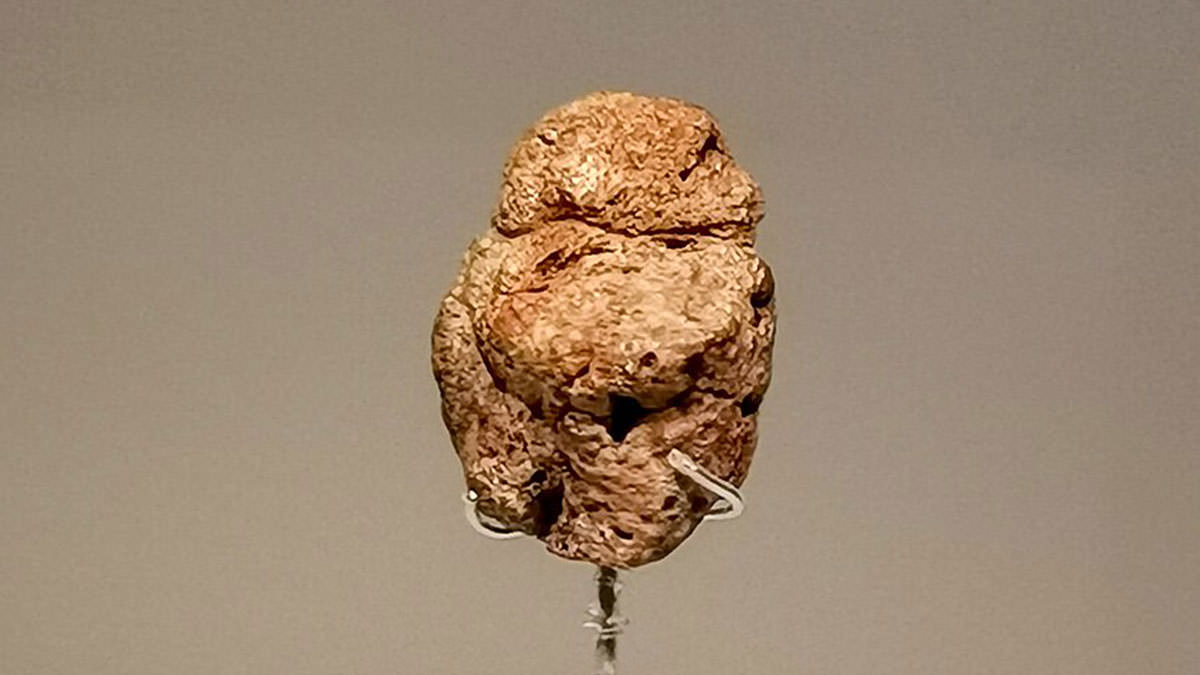
Venus of Berekhat Ram is a pebble which was discovered in Israel in 1981-1982. With an age in excess of 250,000 years, it was probably carved by Homo Erectus. The object resembles a female body and it is now known that it was deliberately modified. Along with the figurine Venus of Tan-Tan, Venus of Berekhat Ram is considered the oldest known human sculpture by many archaeologists.
Table of Contents
The Key Questions
The Berekhat Ram Venus is considered to belong to the Middle Acheulian period. The Acheulian is an archaeological period characterized by the distinctive oval and pear-shaped “hand axes”. It is part of the Paleolithic era. Acheulian tools are older than Neanderthals and were used by Homo Erectus, an extinct species of humans which was last known to be active 108,000 years ago.
The word Paleolithic is a combination of two Greek words palaios (old) and lithos (stone). Also known as the Old Stone Age, Paleolithic era covers almost the entire existence of humans from 2.58 million years ago till around 11,700 years ago. The Lower Paleolithic is the oldest Paleolithic period from c. 3,300,000 – c. 100,000 BCE. The Berekhat Ram Venus belongs to the Lower Paleolithic era.
S1 – Discovery
Berekhat Ram is an archaeological site in Golan Heights, Israel. It gets its name from the Berekhat Ram crater lake in the northernmost part of the Golan Heights. The Venus of Berekhat Ram was discovered by Israeli archaeologist Naama Goren-Inbar during an excavation in 1981-1982 at the site. It was found by an English volunteer which brought it to the notice of Naama Goren-Inbar.
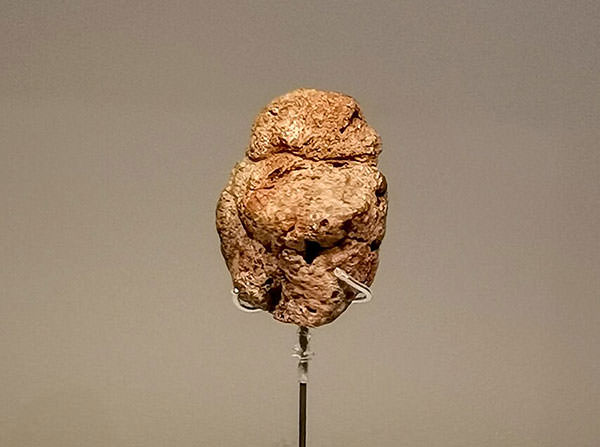

S2 – Description
Naama Goren-Inbar described Venus of Berekhat Ram as a scoria (a kind of volcanic rock) pebble which was rounded and partially weathered with the dimensions: length – 35 mm; width – 25 mm; thickness – 21 mm; and weight 10.33 gm. The pebble was studied by three independent groups of scholars and all of them confirmed that some grooves on the object were made artificially.

The purposely modified parts include two elongated ‘u’ shaped grooves that could have been made to indicate the arms of a human body and abrasion was possibly used to modify some areas, perhaps to suggest breasts. One incision is a deep groove that encircles the narrower end of the pebble, indicating the neck. The only question to categorize the pebble as “art” is whether it was utilitarian or it had a symbolic meaning. Looking at it, it does seem that is was modified for visual appeal.
S3 – Age
Venus of Berekhat Ram has been dated to 230,000 – 700,000 BCE. The date is between these values as it was found sandwiched between two layers of volcanic residue: the upper one was about 230,000 years old and the lower one was approximately 700,000 years old. This suggests that it is older than Neanderthal man, and probably carved by Homo Erectus. Along with the Venus of Tan-Tan, the Berekhat Ram Venus is one of only two artifacts from the Lower Paleolithic period which resemble a human figure.

S4 – The Name Venus?
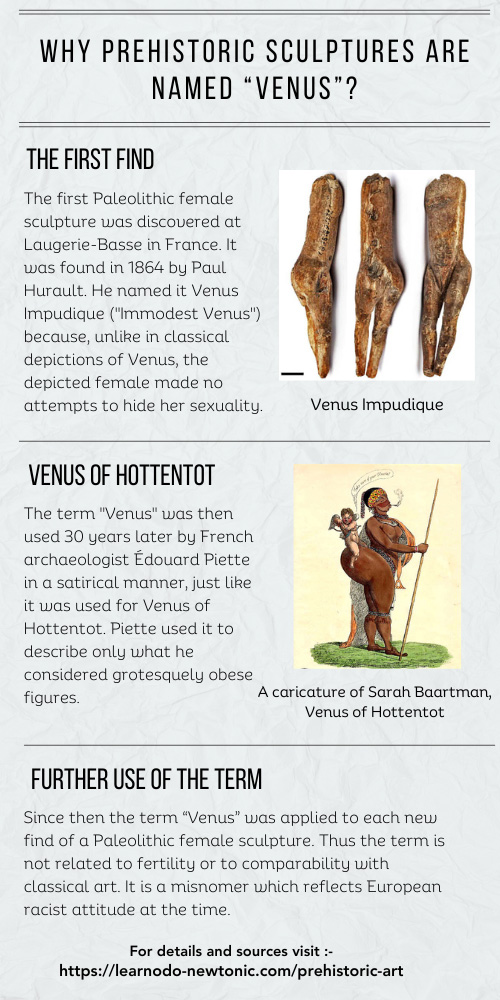
S5 – Paleolithic Art Overview


S6 – Main Sources
S1, S3:-
“The Berekhat Ram Venus”. Don’s Maps.
S2:-
Goren-Inbar, Naama (1986). “A Figurine from the Acheulian Site of Berekhat Ram”. Mitekufat Haeven: Journal of the Israel Prehistoric Society. P7.
Museums as Therapy. (Jun 2, 2021). “Before Art: Lower Paleolithic”. Medium.

